Perfluorinated compounds in the atmosphere of Shenzhen, China
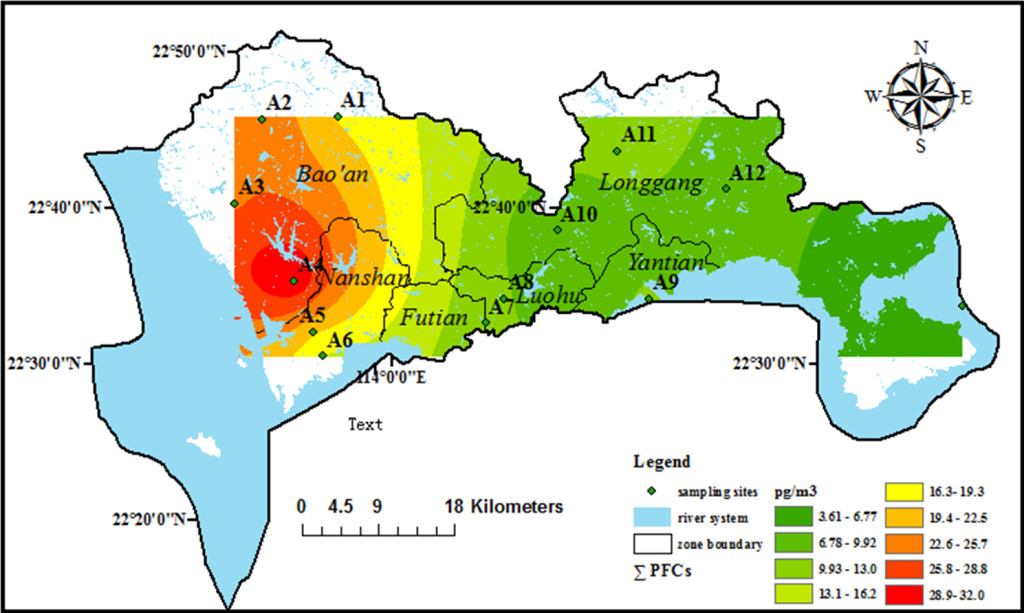
High volume air samples taken to 13 sampling sites that were chosen in 6 districts of Shenzhen, China from September to November, 2011 were analyzed for 11 perfluorinated compounds (PFCs). A set of ionic nonvolatile PFCs including two perfluoroalkyl sulfonic acids (PFSAs, C6 and C8) and perfluoroalkyl carboxylic acids (PFCAs, C4-12) were collected on polyurethane foam – based passive air samplers (PUF – PASs) and determined using high performance liquid chromatography-negative electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC/ESI-MS/MS). PFCs were detected in all air samples, even in the background sample, indicating the widespread contaminations of PFCs in the atmosphere of Shenzhen. Total PFC concentrations (∑ PFCs) of the samples ranged from 3.4 to 34 pg·m-3 with an average of 15 pg·m-3. ∑ PFCs decreased from west to east of Shenzhen, which was related to industrial distribution, population density, and environmental climate (Fig. 1).
Furthermore, Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS) as the two most abundant PFCs averagely accounted for 35% and 22% of ∑ PFCs, respectively. On the base of this data set, the principal component analysis – multiple linear regression model (PCA – MLR) to analyze the sources of atmospheric PFCs, correlation analysis to explore the correlation between ∑ PFCs and levels of atmospheric particulates and mathematical model to calculate environmental health risk assessment were used. This study gives a new method to calculate the sampling rate of PUF – PAS in sampling fine particles for the low volatile POPs.
Zhang H
College of Physics Science and Technology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
Publication
Perfluorinated compounds (PFCs) in the atmosphere of Shenzhen, China: Spatial distribution, sources and health risk assessment.
Liu B, Zhang H, Yao D, Li J, Xie L, Wang X, Wang Y, Liu G, Yang B
Chemosphere. 2015 Nov













Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.