Tag Archives: cardiac
Cardiac autonomic neuropathy: Risk factors, diagnosis and treatment
Cardiac autonomic neuropathy (CAN) is a serious complication of diabetes mellitus (DM) that is strongly associated with approximately five-fold increased risk of cardiovascular mortality. CAN manifests in a spectrum of things, ranging from resting tachycardia and fixed
Decreased vagally-mediated heart rate variability in a conditional NPY Y1 receptor knockout mouse
Women less likely than men to stick to cardiac rehab programs
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death in North America and it occurs more in women than in men. After a sudden heart event, women are more likely than men to die, more likely to have
Nuclear cardiac imaging: the “old grandma” has still something to say
Nerves are required to repair the injured heart
Safety of quinlones reviewed by FDA
Cardiac device lead clots and cardiac ablation: mitigating the potential for Peri-procedural stroke?
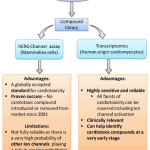
A transcriptomic approach for cardiac (heart) safety assessment
The blue coma: the role of methylene blue in unexplained coma after cardiac surgery
More than 10% of U.S. citizens aged 12 and over take antidepressant medication, and this percentage is mirrored in many other countries. The most commonly prescribed antidepressant drugs are Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), whose mechanism of
The use of multisite ultrasound in cardiac arrest – the SESAME-protocol
ATF3-dependent cross-talk between cardiomyocytes and macrophages promotes cardiac maladaptive remodeling
Cardiovascular diseases are disorders of the heart and blood vessels which are leading to heart failure. Cardiovascular diseases correspond to 30% of all deaths in the world. The molecular processes that undergone from a healthy heart to
Post electric shock cardiac arrest, does it differ?
Sudden cardiac arrest (CA) is a medical emergency that immediately causes circulatory failure with loss of consciousness; absence of breathing; low blood pressure with no pulses; and no heart sounds. The most common causes of CA are electrical
Two essential cardiac disorders improvement in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
The effect of a hydrogen sulfide releasing molecule on the cold storage of livers from dead donor rats
What does the PROMISE trial mean for cardiac CT?
Survivals in pediatric cardiac tamponade caused by central venous catheters
Pediatric central venous catheter (CVC) placement is used for fluid or drug administration and is useful for hemodynamic (the fluid dynamics of flow) management in cardiac surgery but associated with complications such as rare but serious cardiac